Task Manager is a powerful control center for unraveling a wealth of information about a computer’s performance. Plus, it’s incredibly user-friendly!
Many Windows users treat the Task Manager as an unsolvable mystery that should remain untouched.
Big mistake! Understanding Task Manager can help you learn how your computer and its operations work. Furthermore, it’s an extraordinary tool for solving common issues that affect system performance.
Once you know how to read it, you can feel like an almighty overseer handling all its functions. Interested? Let’s proceed to our guide on all its features!
How to run Task Manager
There are a few methods of launching Task Manager. The most popular one is the Ctrl+Alt+Delete keyboard shortcut.
After pressing these keys, a new window appears, from which you can select Task Manager. You can also use a faster way – Ctrl+Shift+Escape.
However, if keyboard shortcuts are not your thing or you have trouble memorizing them, right-click the Start button and pick Task Manager from the list of available options.
What not to do
Terminating some tasks can lead to permanent crashes or failures. Therefore, always use Task Manager with caution and don’t make changes you are unsure about.
If you find yourself trying to solve a problem involving its tools but don’t know how, use the detailed information on the official Microsoft support website – https://support.microsoft.com/en-us.
Alternatively, consult your computer service to fix the issue.
Task Manager Tabs Explained
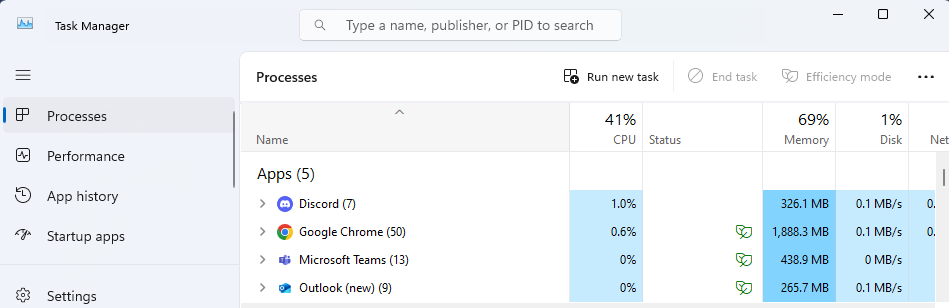
Processes
After launching Task Manager for the first time, you’ll see a list of active programs and tasks on your computer.
That’s where you can end unresponsive apps and restart them to fix the problem. It’s also the best place to examine their CPU and memory usage to locate the most resource-consuming ones.
Performance
The „Performance” tab is like your computer’s pulse. Here, you can monitor and control all vital data, including network, memory, CPU, or disk resource usage.
With this information, you can locate culprits of eventual bottlenecks and prevent slow system performance.
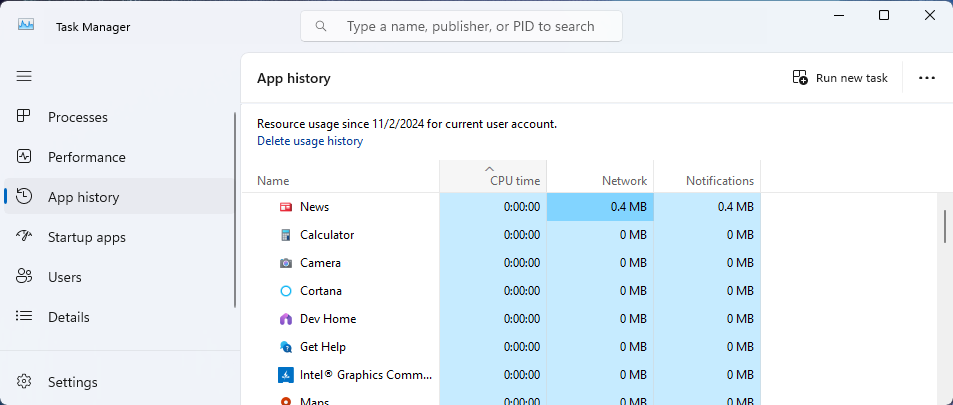
App History
The “App History” tab provides an overview of the total resources used by individual applications since Windows installation.
It’s the best feature for monitoring program performance, as it lets you target apps overusing network bandwidth. Use this tab to analyze application data affecting your Internet speed.
Startup Apps
The “Startup Apps” provides a detailed view of the features related to the startup items on your system.
You can analyze all the apps launching when your operating system starts. As you can probably guess, it helps to find all the operations affecting the overall computer’s performance.
If your PC is starting up slowly, it could be that some applications delay the process. Use the “Startup Apps” to find details about their resource usage and turn them off. To do that, click the app and choose to disable it from the available options.
Users
Exploring the “Users” tab, you can identify which user account is associated with each running process.
Use this option to log out another user, view apps running on other user accounts, or switch to another user account. This way, you have perfect control over resource management on the device, regardless of the account.
Details
This tab unravels a complete list of all active tasks but in a more detailed version than the ones mentioned above.
Here, you can analyze vital data like memory working set, CPU time, session ID, base priority, handles, threads, and I/O reads and writes, allowing you to learn how specific processes affect the operating system’s performance.
Services
The “Services” tab provides a comprehensive overview of all running services and their status. Depending on their status, you can use this option to start or stop services, troubleshoot issues, and better manage system resources.
Click the chosen service to explore more detailed information, like startup types and descriptions.
Methods of resolving the most common issues with Task Manager
Unresponsive Programs
Nothing disrupts your workflow like a freezing application. Luckily, you can quickly fix this problem using the Task Manager.
Launch it as described in the “How to run Task Manager” section, go to the “Processes” tab, and find the unresponsive application in the list of active tasks.
Once you right-click on the problematic program, select “End task”. You can then restart the closed program and resume your work.
Slow System Performance
Launch the Task Manager and go to the “Performance” tab. In this section, you can view information about apps’ memory, CPU, and disk usage to identify those devouring too many of your operating system resources.
Slow boot times
So you have found your computer starting up slowly and don’t know what to do. Don’t worry, as the “Startup” tab comes to the rescue.
All you need to do is explore the list of programs on this tab and disable the most resource-hungry ones. Getting rid of them should significantly speed up startup times and positively impact system performance.
Conclusion
It’s awesome how Task Manager allows any user, regardless of technical knowledge, to understand operations within the system.
Using our guide, even beginners can discover a wide range of new possibilities for managing the operating system and always remain in control of its best performance.